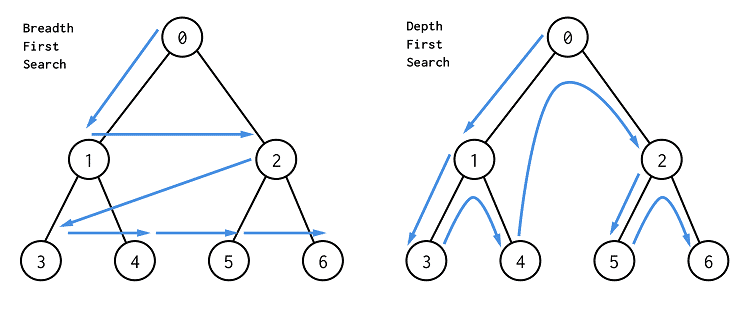
In Data Structures (DS), BFS (Breadth-First Search) and DFS (Depth-First Search) are two fundamental graph traversal algorithms used to explore nodes in a graph or tree. Breadth-First Search (BFS) BFS explores a graph level by level, starting from a selected node and visiting all its neighbors before moving on to their …
Read More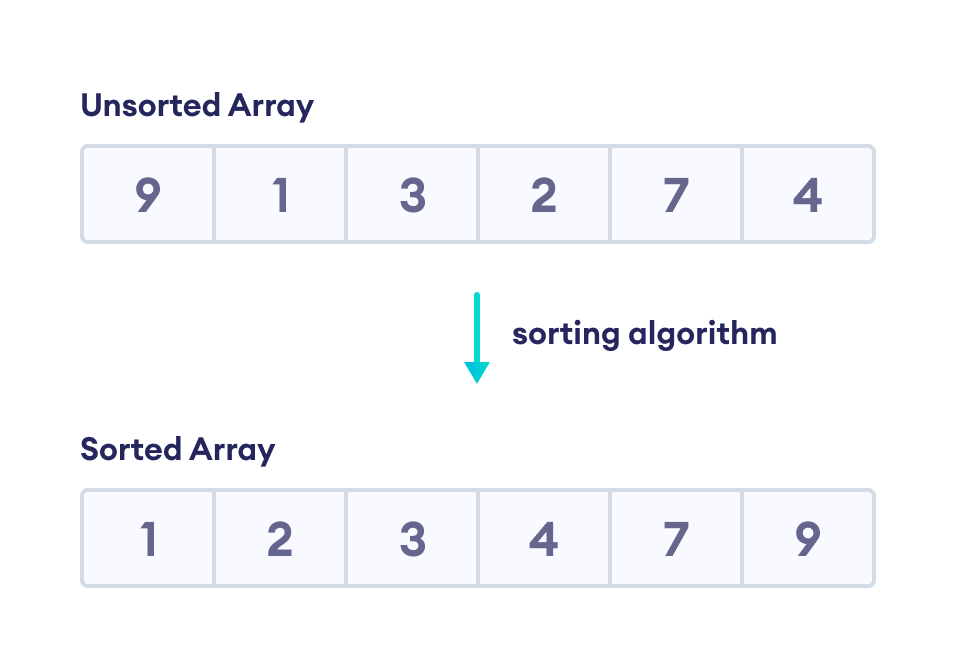
Merge Sort in Data Structures Merge Sort is a popular Divide and Conquer algorithm used to sort arrays or lists efficiently. It works by recursively dividing the array into smaller halves, sorting them, and then merging the sorted halves back together. ⚙️ How Merge Sort Works Divide: Split the array into two halves …
Read More
Here, you can find some basic Java example codes to help you get started. These examples cover a variety of fundamental concepts and are great for beginners looking to practice and learn. 1-D 1class D1 2{ 3public static void main(String[] args) 4{ 5int month_days[]; 6month_days=new int[12]; 7month_days[0]=31; …
Read More
Super and This keywords of Java Super Keyword: Definition: super is a reference to the immediate parent class of the current object. It is mainly used in the context of inheritance. Usage: Call the parent class's constructor: super() can be used to call the constructor of the parent class. This is often used to …
Read More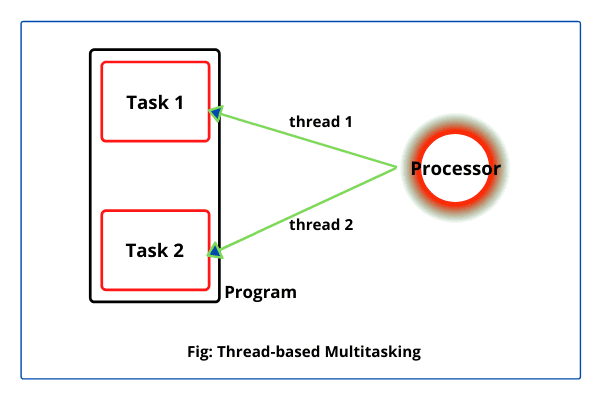
Multithreading in Java is a powerful feature that allows concurrent execution of two or more threads within a program. A thread is a lightweight subprocess and the smallest unit of processing, and multithreading helps improve the performance and efficiency of applications, especially those requiring multiple …
Read More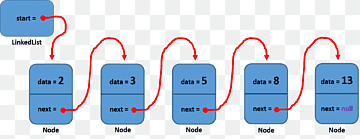
A linked list is a fundamental data structure used in computer science to organize and store a collection of elements. Unlike arrays, linked lists do not require a contiguous block of memory and can efficiently handle dynamic memory allocation. Key Characteristics Nodes: A linked list is composed of nodes, where each …
Read More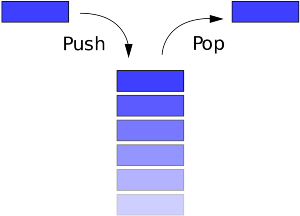
A stack is a fundamental data structure in computer science that operates on a Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle. This means that the last element added to the stack is the first one to be removed. You can think of a stack like a stack of plates: you add new plates to the top and remove them from the top as well. Key …
Read More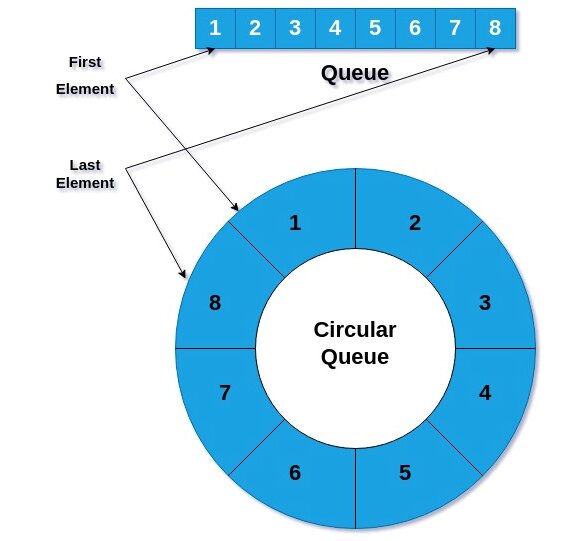
A circular queue is a data structure that operates on a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) basis but with a circular arrangement. Unlike a linear queue, where elements are added at the rear and removed from the front, a circular queue connects the last position back to the first, forming a circle. This allows for efficient use …
Read More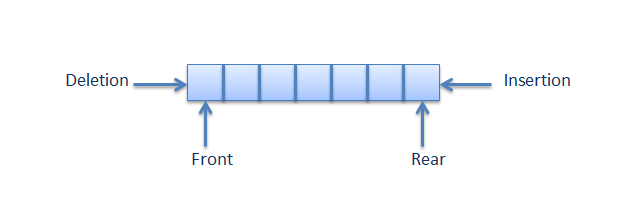
A simple queue is a fundamental data structure that follows the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) principle. This means that the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed, just like people standing in line—whoever gets in first is served first. Key Operations in a Simple Queue: Enqueue (Insertion): …
Read More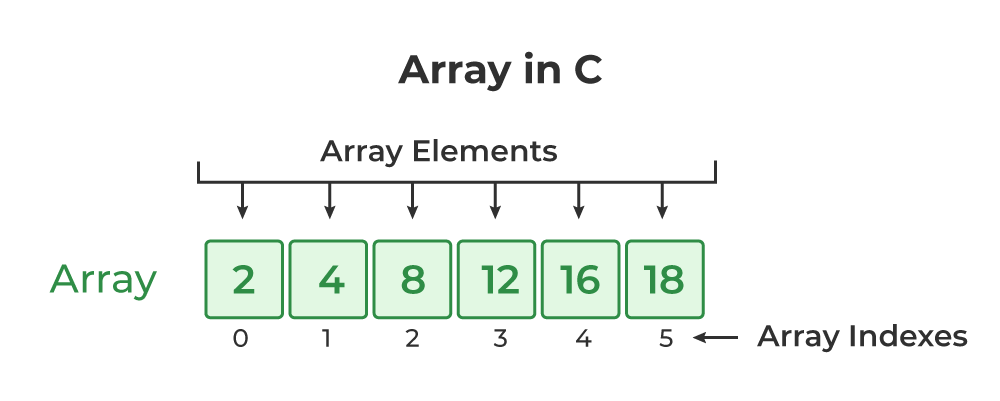
An array is a data structure used in programming to store a collection of elements, typically of the same type, in a fixed-size sequence. Initialisation of Array 1#include <stdio.h> 2int main() 3{ 4 // it's not important to give size during initialisation. 5 // eg: float y[]={1.2,2,3.32}; 6 7 int g[5]; 8 int …
Read More