Circular Queue
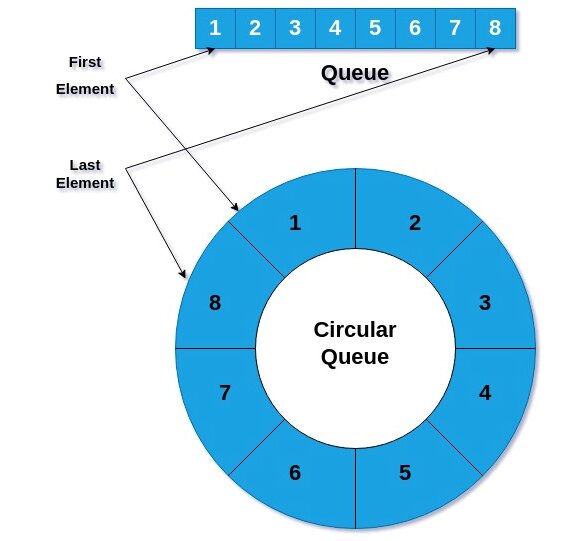
A circular queue is a data structure that operates on a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) basis but with a circular arrangement. Unlike a linear queue, where elements are added at the rear and removed from the front, a circular queue connects the last position back to the first, forming a circle. This allows for efficient use of space by reusing empty positions once elements are dequeued.
Key Points:
Fixed Size: The queue has a predefined capacity.Circular Structure: When the rear reaches the end, it wraps around to the beginning if space is available.Efficient Space Utilization: It avoids wasting memory by utilizing free space once items are removed.
Key Operations:
Enqueue: Add an element to the rear.Dequeue: Remove an element from the front.isFull: Check if the queue is full.isEmpty: Check if the queue is empty.
Example
For a queue of size 5:
Initially: [ , , , , ]
After Enqueue(1), Enqueue(2): [1, 2, , , ]
After Dequeue(): [ , 2, , , ]
Enqueue(3), Enqueue(4), Enqueue(5): [ , 2, 3, 4, 5]
Enqueue(6) wraps around: [6, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Applications
Memory buffers, task scheduling, and network data handling where efficient use of limited space is important.
Program
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <stdlib.h>
3#define max 6
4int queue[max];
5int front = -1;
6int rear = -1;
7void enqueue(int element)
8{
9 if (front == -1 && rear == -1)
10 {
11 front = 0;
12 rear = 0;
13 queue[rear] = element;
14 }
15 else if ((rear + 1) % max == front)
16 {
17 printf("Queue is full");
18 }
19 else
20 {
21 rear = (rear + 1) % max;
22 queue[rear] = element;
23 }
24}
25int dequeue()
26{
27 if ((front == -1) && (rear == -1))
28 {
29 printf("\nQueue is empty");
30 }
31 else if (front == rear)
32 {
33 printf("\nThe dequeued element is %d", queue[front]);
34 front = -1;
35 rear = -1;
36 }
37 else
38 {
39 printf("\nThe dequeued element is %d", queue[front]);
40 front = (front + 1) % max;
41 }
42}
43void display()
44{
45 if (front == -1 && rear == -1)
46 {
47 printf("Queue is empty\n");
48 }
49 else
50 {
51 printf("Elements in the queue are: ");
52 int i = front;
53 while (1)
54 {
55 printf("%d ", queue[i]);
56 if (i == rear)
57 {
58 break;
59 }
60 i = (i + 1) % max;
61 }
62 printf("\n");
63 }
64}
65
66void main()
67{
68 int ch, x;
69
70 while (1)
71 {
72 printf("\n1.Enqueue");
73 printf("\n2.Dequeue");
74 printf("\n3.Display");
75 printf("\n4.Exit");
76 printf("\nEnter your choice:");
77 scanf("%d", &ch);
78 switch (ch)
79 {
80 case 1:
81 printf("Enter the data:\n");
82 scanf("%d", &x);
83 enqueue(x);
84 break;
85 case 2:
86 dequeue();
87 break;
88 case 3:
89 display();
90 break;
91 case 4:
92 exit(0);
93 break;
94 default:
95 printf("Invalid Operator");
96 }
97 }
98}