DS - Stack
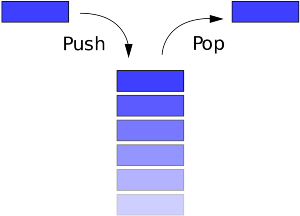
A stack is a fundamental data structure in computer science that operates on a Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle. This means that the last element added to the stack is the first one to be removed. You can think of a stack like a stack of plates: you add new plates to the top and remove them from the top as well.
Key Operations
Push: Add an element to the top of the stack.Pop: Remove the element from the top of the stack.Peek (or Top): Retrieve the element at the top of the stack without removing it.IsEmpty: Check if the stack is empty.
Characteristics
LIFO Order: The most recently added element is the first one to be removed.Dynamic Size: In many implementations, a stack can grow or shrink as needed, depending on the underlying data structure (such as an array or linked list).
Programs:
Implementation of Stack.
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <stdlib.h>
3#define SIZE 4
4
5int top = -1, inp_array[SIZE];
6void push();
7void pop();
8void show();
9
10int main()
11{
12 int choice;
13
14 while (1)
15 {
16 printf("\nPerform operations on the stack:");
17 printf("\n1.Push the element\n2.Pop the element\n3.Show\n4.End");
18 printf("\n\nEnter the choice: ");
19 scanf("%d", &choice);
20
21 switch (choice)
22 {
23 case 1:
24 push();
25 break;
26 case 2:
27 pop();
28 break;
29 case 3:
30 show();
31 break;
32 case 4:
33 exit(0);
34
35 default:
36 printf("\nInvalid choice!!");
37 }
38 }
39}
40
41void push()
42{
43 int x;
44
45 if (top == SIZE - 1)
46 {
47 printf("\nOverflow!!");
48 }
49 else
50 {
51 printf("\nEnter the element to be added onto the stack: ");
52 scanf("%d", &x);
53 top = top + 1;
54 inp_array[top] = x;
55 }
56}
57
58void pop()
59{
60 if (top == -1)
61 {
62 printf("\nUnderflow!!");
63 }
64 else
65 {
66 printf("\nPopped element: %d", inp_array[top]);
67 top = top - 1;
68 }
69}
70
71void show()
72{
73 if (top == -1)
74 {
75 printf("\nUnderflow!!");
76 }
77 else
78 {
79 printf("\nElements present in the stack: \n");
80 for (int i = top; i >= 0; --i)
81 printf("%d\n", inp_array[i]);
82 }
83}
Stack using Linked List:
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <stdlib.h>
3
4// Define the structure of a node in the linked list
5struct Node {
6 int data;
7 struct Node* next;
8};
9
10// Function to create a new node
11struct Node* newNode(int data) {
12 struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
13 node->data = data;
14 node->next = NULL;
15 return node;
16}
17
18// Function to check if the stack is empty
19int isEmpty(struct Node* top) {
20 return top == NULL;
21}
22
23// Function to push an element onto the stack
24void push(struct Node** top, int data) {
25 struct Node* node = newNode(data);
26 node->next = *top;
27 *top = node;
28 printf("%d pushed to stack\n", data);
29}
30
31// Function to pop an element from the stack
32int pop(struct Node** top) {
33 if (isEmpty(*top)) {
34 printf("Stack underflow\n");
35 return -1;
36 }
37struct Node* temp = *top;
38 int popped = temp->data;
39 *top = (*top)->next;
40 free(temp);
41 return popped;
42}
43
44// Function to peek the top element of the stack
45int peek(struct Node* top) {
46 if (isEmpty(top)) {
47 printf("Stack is empty\n");
48 return -1;
49 }
50 return top->data;
51}
52
53// Function to display the stack
54void display(struct Node* top) {
55 if (isEmpty(top)) {
56 printf("Stack is empty\n");
57 return;
58 }
59 struct Node* temp = top;
60 printf("Stack elements: ");
61 while (temp != NULL) {
62 printf("%d ", temp->data);
63 temp = temp->next;
64 }
65 printf("\n");
66}
67int main() {
68 struct Node* stack = NULL; // Initialize the stack to NULL (empty stack)
69
70 // Testing stack operations
71 push(&stack, 10);
72 push(&stack, 20);
73 push(&stack, 30);
74 display(stack); // Expected output: 30 20 10
75
76 printf("Popped: %d\n", pop(&stack)); // Expected output: 30
77 display(stack); // Expected output: 20 10
78
79 printf("Top element: %d\n", peek(stack)); // Expected output: 20
80
81 pop(&stack); // Popping 20
82 pop(&stack); // Popping 10
83 pop(&stack); // Stack underflow
84
85 return 0;
86}